Key highlights
1
Many key parts work together to ensure the engine delivers optimum performance
2
Car engines run on four stroke cycle - intake, compression, power and exhaust
3
Proper engine maintenance is required for optimum efficiency and extended life
- The Four Stroke Cycle of Car Engine
- Key Components of a Car Engine
- Car Engine Maintenance Tips
- Common Engine Problems
- Types of Car Engines
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Key highlights
1
Many key parts work together to ensure the engine delivers optimum performance
2
Car engines run on four stroke cycle - intake, compression, power and exhaust
3
Proper engine maintenance is required for optimum efficiency and extended life
Akash Vashisth
The engine is the heart of your car, turning fuel into power that drives your vehicle. Without it, your car simply wouldn’t run. Though the engine might seem complex, getting familiar with its key parts and how they function can simplify maintenance and help you spot issues early. Understanding your engine not only keeps your car performing at its best but can also save you time and money in the long run.
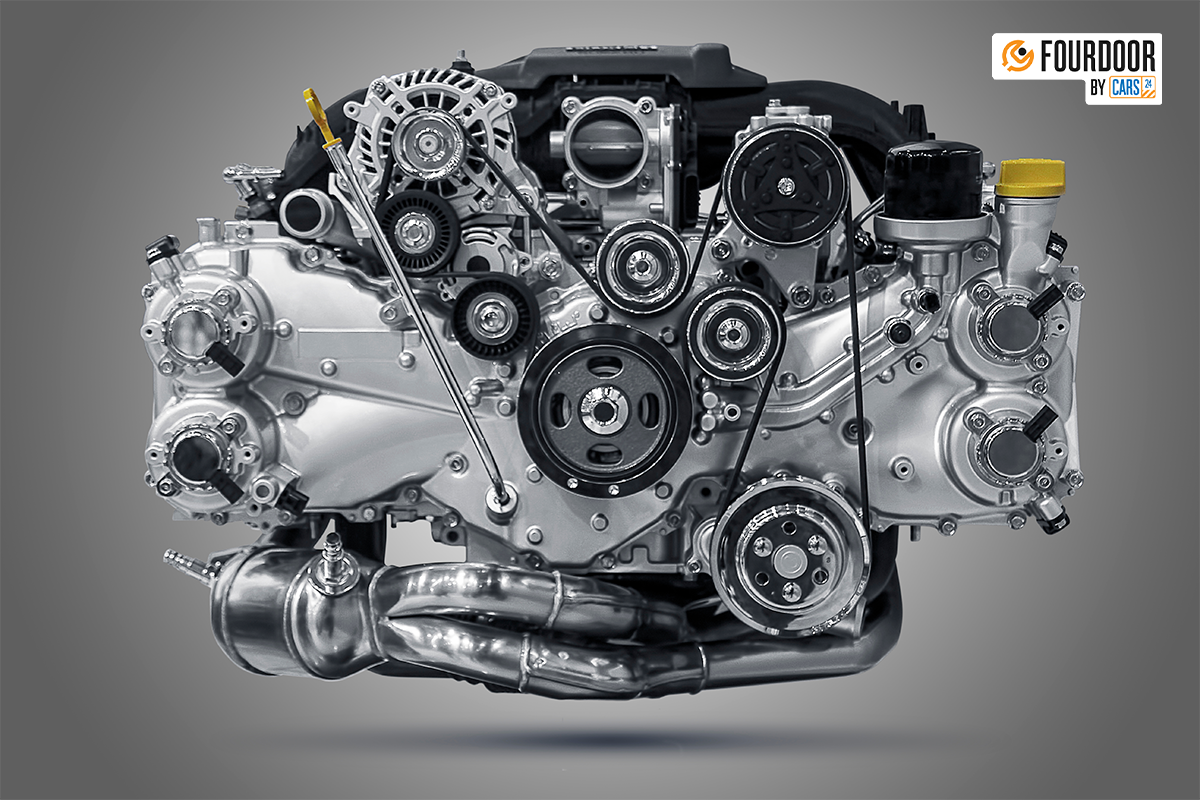
Key Components of a Car Engine
A car engine comprises several important components that work together to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Here’s a brief overview of each part:
- Cylinders: Cylinders are the chambers where fuel is burned and power is produced. Most cars have three or four cylinders. Premium and sports cars have anything from six to twelve cylinders. Also the arrangement of cylinders affect the engine’s performance.
- Pistons: Pistons inside the cylinders move up and down as fuel combusts. Their movement is what rotates the crankshaft.
- Connecting rod: Connecting rod links the pistons to the crankshaft, converting the piston’s vertical movement into rotational motion of the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into the rotational movement that is required to turn your car’s wheels.
- Piston rings: Piston rings seal the gap between the piston and the cylinder walls. This seal prevents the leakage of gases from the combustion chamber into the crankcase and leakage of oil into the combustion chamber.
- Valves: Valves allow the fuel and air into the cylinders and allow exhaust gases to escape after combustion.
- Camshaft: The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves, ensuring the right amount of fuel and air enters the cylinders at the right time.
- Timing belt/chain: Timing chain or belt ensures that the crankshaft and camshaft rotate in sync so that the valves open and close at the correct time during the combustion process.
- Spark plugs: Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinder to start the combustion process. These are only found in petrol engines.
- Fuel injectors: In petrol engines, fuel injectors inject the fuel into the intake manifold, where it mixes with air and is sucked into the combustion chamber or directly into the combustion in case of Gasoline Direct Injection engines. In diesel engines, the fuel injectors deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, where it is compressed and ignited.
- Lubrication system: A lubrication system distributes oil to all moving parts to minimise friction and wear.
- Exhaust system: Once fuel is burned, the exhaust system routes the burnt gases into the atmosphere through the tailpipe.
The Four Stroke Cycle of Car Engine
Now that you know the main parts, let’s explore how they all work together. A car engine follows a process called the four-stroke cycle, which consists of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
- Intake: The intake valve opens, allowing a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder as the piston moves downward. In diesel engines, only air is introduced into the combustion chamber during the intake stroke.
- Compression: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves upward, compressing the fuel-air mixture. In diesel engines, only the air is compressed during this stroke.
- Combustion: The spark plug ignites the compressed mixture of petrol and air, causing an explosion that forces the piston back down. In case of diesel engines, the injectors inject highly pressurised diesel fuel into the combustion chamber causing it to automatically burn due to high temperature of compressed air.
- Exhaust: This stroke is the same for both petrol and diesel engines. The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves upward again, pushing the burnt gases out of the cylinder.
This four-stroke cycle repeats thousands of times per minute to provide optimum power to your vehicle. All the parts of your car engine work in unison to deliver the expected driving experience.
Types of Car Engines
Many types of car engines exist, all with unique features and benefits:
- Inline engines: Inline engines are usually seen in compact and midsize cars, with cylinders set up in a straight line. They're recognized for being cost-effective and easy to maintain.
- V-type: V engines are structured with cylinders in two banks, creating a V-like shape. The bank angle can range from 45 degrees to 90 degrees, and these engines are used in high-performance cars.
- Boxer engines: The cylinders in a boxer engine are arranged in a horizontal manner and opposite to each other. Because of their flat shape, they contribute to the reduction of the car's centre of gravity which results in better control on the road.
While these are the most common engine layouts, there are other engine types such as VR, W, Slant, and others which are no longer in production or rarely produced for high-end hand-made cars.
Common Engine Problems
Even the most modern and well-maintained engines can experience issues. Here are some common engine problems:
- Overheating: Overheating in the engines is usually caused by low coolant levels or a malfunctioning thermostat. Prevent this by regularly checking your coolant and avoiding overloading your engine.
- Misfiring: Misfiring occurs due to faulty spark plugs or fuel system issues. Replacing spark plugs, inspecting the timing and the fuel system can solve this problem.
- Oil Leaks: Oil leaks are typically caused by worn-out seals or gaskets. Regular oil changes and proper engine inspections can help detect issues early.
Car Engine Maintenance Tips
Regular engine maintenance is essential to keep your car running smoothly. Here are some tips:
- Regular oil changes: Oil is vital for keeping engine parts lubricated and reducing friction. To prevent wear and tear, change your engine oil according to your manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Checking coolant levels: Your engine's cooling system prevents overheating. Check your coolant levels regularly and top them off if needed.
- Monitoring engine warning lights: Pay attention to warning lights on your dashboard. They can indicate low oil pressure, overheating, or faulty sensors.
- Inspecting belts and hoses: Check your engine’s belts and hoses for signs of wear. Replacing belts and hoses on time can prevent breakdowns.
- Cleaning or replacing air filter: A clean air filter ensures your engine gets the right air for combustion. Dirty or clogged air filters can reduce engine performance and efficiency.
- Regular tune-ups: Periodic engine tune-ups ensure that all components are working correctly and can help identify potential issues at an early stage.
Conclusion
Understanding your car engine's parts and how they work can help you keep your vehicle in great condition. Having the right knowledge about the key components and their functions will allow you to perform routine maintenance, identify potential issues, and extend the life of your car’s engine. Regular engine care is essential to keep your car running smoothly and avoid costly repairs in the future.
FAQs
Q. What are the main components of a car engine?
The main components of a car engine include cylinders, pistons, connecting rods, crankshafts, camshafts, valves, piston rings, spark plugs, fuel injectors, the lubrication system, and the exhaust system. These parts work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy, powering the vehicle.
Q. How does a four-stroke engine cycle work?
A four-stroke engine cycle consists of four stages: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. In the first stroke, the intake valve opens, allowing air and fuel to enter. The second stroke compresses the mixture, and the spark plug ignites it in the third stroke to produce power. Finally, in the fourth stroke, the exhaust valve opens and burnt gases are expelled.
Q. What are the different types of car engines?
The most common types of car engines include inline engines (cylinders in a straight line), V-type engines (cylinders arranged in a V shape), boxer engines (horizontally opposed cylinders), VR-type engines (V-shaped engines with narrow bank angle), and W-type engines (two VR-type rows combined). Each engine type offers different performance characteristics.
Q. What are common car engine problems?
Some common engine problems include overheating, misfiring, oil leaks, worn-out belts, dead battery, poor lubrication, excessive exhaust fumes, unusual noises, etc.
Q. How can I maintain my car engine to ensure longevity?
To maintain reliability of your car engine you need to change engine oil regularly, check coolant levels, monitor dashboard warning lights, inspect belts and hoses, keep the air filter clean, and do not redline frequently. These simple steps can help keep your engine running smoothly and prevent major issues.